Rural Healthcare
Bring Specialist-Level Care to Underserved Communities
The Rural Healthcare Challenge
Problems
Shortage of specialist doctors in rural areas
Patients must travel hours to reach tertiary care hospitals
Lack of diagnostic equipment in primary health centers
High cost and time burden on patients
Delayed diagnosis leads to worse outcomes

Global Impact
- 45% of global population lives in rural areas
- 50% have no access to essential health services
- Rural mortality rates 30-40% higher than urban
- Financial hardship from medical travel and lost wages

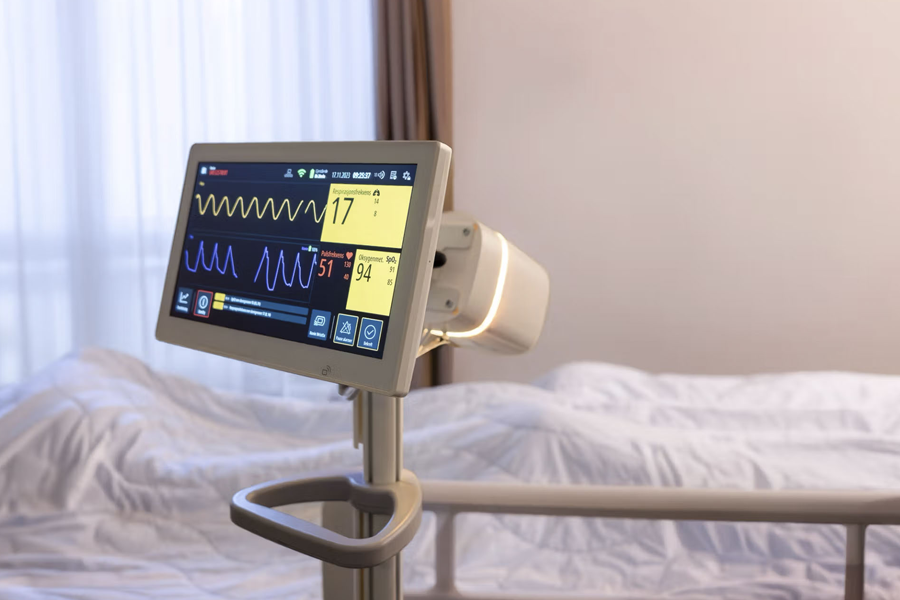
How It Works
- Paramedic uses devices to collect vitals
- Data transmitted in real-time during video consultation
- Specialist sees live vitals on screen
- AI assists with preliminary analysis
- Devices work on battery power (for areas with unreliable electricity)

Results
- 80% reduction in patient referral time — Fewer unnecessary transfers to cities
- 60% decrease in patient travel costs — Families save money, avoid lost wages
- 1,000+ patients/month receive specialist consultations remotely
- 150+ complications prevented through early AI-detected warnings
- 40% improvement in chronic disease management — Hypertension, diabetes better controlled with remote monitoring
Government & NGO Deployment
National Health Programs
Integrate with government telemedicine initiatives
Connect to national health missions (e.g., India’s ABDM)
Support universal health coverage goals
Data for public health surveillance (disease outbreaks, epidemic tracking)
National Health Programs
Integrate with government telemedicine initiatives
Connect to national health missions (e.g., India’s ABDM)
Support universal health coverage goals
Data for public health surveillance (disease outbreaks, epidemic tracking)
NGO Partnerships
Deploy in NGO-run health centers
Training programs for community health workers
Subsidized/free care for underserved populations
Grant-funded equipment and infrastructure
NGO Partnerships
Deploy in NGO-run health centers
Training programs for community health workers
Subsidized/free care for underserved populations
Grant-funded equipment and infrastructure
Financial Models
Government-funded: Free for patients, government pays per consultation
Micro-insurance: Community health insurance schemes cover telemedicine
Cross-subsidy: Urban patients subsidize rural care
NGO grants: Philanthropic funding for equipment and operations
Financial Models
Government-funded: Free for patients, government pays per consultation
Micro-insurance: Community health insurance schemes cover telemedicine
Cross-subsidy: Urban patients subsidize rural care
NGO grants: Philanthropic funding for equipment and operations
Injury Prevention
- Stretch break reminders
- Video tutorials for proper workstation setup
- Preventive exercises
Benefits
For Patients
- Access to specialists — Without traveling hours
- Lower costs — Eliminate travel, accommodation expenses
- Faster care — Immediate consultation, not weeks-long wait for appointment
- Better outcomes — Early diagnosis, proper treatment
- Family impact — Less disruption to work, childcare
For Patients
Biometric screening — Blood pressure, BMI, body composition
Lab work — Lipid panel, glucose, HbA1c, liver/kidney function
AI vital scanning — Stress, HRV, cardiovascular health
Risk scoring — Predict diabetes, hypertension, cardiac disease
For Healthcare Systems
- Access to specialists — Without traveling hours
- Lower costs — Eliminate travel, accommodation expenses
- Faster care — Immediate consultation, not weeks-long wait for appointment
- Better outcomes — Early diagnosis, proper treatment
- Family impact — Less disruption to work, childcare
For Healthcare Systems
- Efficiency — Specialists serve more patients without physical travel
- Cost-effective — Lower infrastructure costs than building hospitals everywhere
- Scalability — Add more spokes without proportional cost increase
- Data for planning — Disease burden data guides resource allocation
- Equity — Fulfill constitutional right to health for all citizens
For Society
- Access to specialists — Without traveling hours
- Lower costs — Eliminate travel, accommodation expenses
- Faster care — Immediate consultation, not weeks-long wait for appointment
- Better outcomes — Early diagnosis, proper treatment
- Family impact — Less disruption to work, childcare
For Society
- Reduced mortality — Especially maternal, child, cardiac
- Economic productivity — Healthier workforce
- Migration reduction — People don’t move to cities for healthcare
- Epidemic control — Early detection and response to outbreaks